Although our mind is constantly trying to make sense of the world around us it can sometimes get a little out of control and make us start to see things literally.
While, some of the optical illusions on our list are relatively famous, others are a bit more obscure but all of them give us a glimpse into our amazingly complex minds.
There is no magic involved, no strings attached, its all in your head. Here we go.
Rotating Rings : If you stare at the dot in the center and move your head away from the screen the rings will start to rotate. Now gradually get closer again…they change direction!
Hermann Grid : If you stare at the dot in the center and move your head away from the screen the rings will start to rotate. Now gradually get closer again…they change direction!
Fading Image: Stare at the image for about half a minute without moving your eyes and watch as it gradually disappears. This is a variation of Troxler’s effect which essentially says that if you fixate your eyes on a certain point, stimuli near that point will gradually fade.
Kanizsa Triangle: The Kanizsa Triangle was named after the psychologist Gaetano Kanizsa who first described its effect. When you look at the image your brain creates contours (outlines) of a triangle although none exist. In reality it is an illusion created by the the wedges and the angles.
Blivet: This is a rather famous illusion of an impossible object. It has two rectangular prongs at one end that morph into three cylindrical prongs at the other.
Monster Illusion: Found in virtually every psychology textbook in the world, the two monsters in this illusion are in fact the same size. Your brain automatically adjusts images that it perceives to be distant in order to compensate for the fact that they are larger than they seem.
Jastrow Illusion : Named after Robert Jastrow in 1889, the bottom figure appears to be larger although they are both the same size. This is because the shorter edge of “A” is directly adjacent to the longer edge of “B”.
Fraser Spiral : First described by British psychologist James Fraser in 1908, this illusion is also known as the “false spiral”. While it appears that the overlapping arcs are spiralling into infinity they are in fact only a series of concentric circles.
Scintillating Grid: This is a variation of the Hermann Grid where black dots appear and disappear at the intersections of the gray lines. Interestingly enough, if you cock your head at a 45 degree angle the effect is reduced (but not eliminated).
Blue vs Green: There are several variations to this illusion but the effect is the same. The “blue” and “green” backgrounds are in fact the same color (open it in photoshop).
Endless Staircase: This is a variation of the endless staircase illusion constructed out of legos. Like the the blivet, this is also an impossible object and is sometimes called the “Penrose triangle”.
Black on White: Stare at the center of the image for about 30 seconds and then look away at a preferably white surface (sometimes the ceiling works). What do you see?
Zöllner Illusion: This illusion was named after Johann Karl Friedrich Zöllner and consists of parallel lines that appear to be diagonal. You may need a ruler for this one.
Hering Illusion: Although the two red lines seem to be bowed outwards they are perfectly straight and parallel. This illusion is attributed to Ewald Hering, a German physiologist who believed that the distortion was derived from the mind overestimating the angles at the points of intersection.
Titchener Circles : Also known as the Ebbinghaus Illusion, there is still a debate in psychological circles as to the exact mechanism and implication of this effect. Essentially, however, the orange circle on the left appears to be smaller than the one on the right although in reality they are the same size.
Leaning Tower: Yes, the leaning tower of pisa does actually lean, but these two images are in fact one and the same. Although the image on the right appears to be leaning away from the one on the left this is only in your head. Go ahead and try the same thing with the empire state building…it will lean too, promise.
Wonder Block : Yet again we have an example of an impossible object except this time it’s the rotation of the blocks that is inconsistent. Are they side by side or on top of each other? Maybe thats why they call them indecipherable figures.
Floating Stairs: For centuries artists have been pushing our perceptual limits and if you ever get lucky enough, from the right angle, you may just catch a glimpse into the practical artistic applications of optical illusions and the way our mind interprets them.
Spinning Silhouette: Created by web designer Nobuyuki Kayahara, some people at first see the figure spinning clockwise while others see it spinning counterclockwise. Don’t spend too much time trying to decipher it though, you could be here all day.
Up and Down: Although it is obvious that the pillars are staying in the same horizontal position, our brain is convinced that they should be moving to the right.
Rotating Squares: At first this one may be hard to see, but if you begin to scan back and forth across the image you will notice that the squares in your periphery begin to rotate. As soon as your eyes stop moving, however, rotation will cease.
Static Motion: No, this is not an animated GIF. The image really is static. Notice that when you look at any individual point dead on, it will stop moving. This powerful illusion is derived from interacting color contrasts and shape positions within the image.
Lilac Chaser: Also known as the pac-man illusion, if you stare at the center cross for a couple seconds you will begin to perceive a green disco going around the circle of magenta discs. After a few more seconds the magenta discs will gradually begin to fade away until all you see a green disc going in a circle around the cross (if you’re having trouble seeing it move closer to the screen).
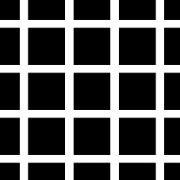
Cafe Illusion: Another famous illusion, this one was recently rediscovered in a cafe wall at the bottom of St. Michael’s Hill. Although the lines appear to be diverging from one another they are in fact quite parallel.
Checker Shadow Illusion : Probably one of the most unbelievable illusions out there, this one was first published by Edward Adelson, a professor at MIT. Although the square labeled “A” appears to be darker than the square labeled “B”, they are actually exactly the same shade of gray. Its okay if you don’t believe it, we didn’t either, but Photoshop proved us wrong.
























No comments:
Post a Comment